Technology for the production of plastic containers
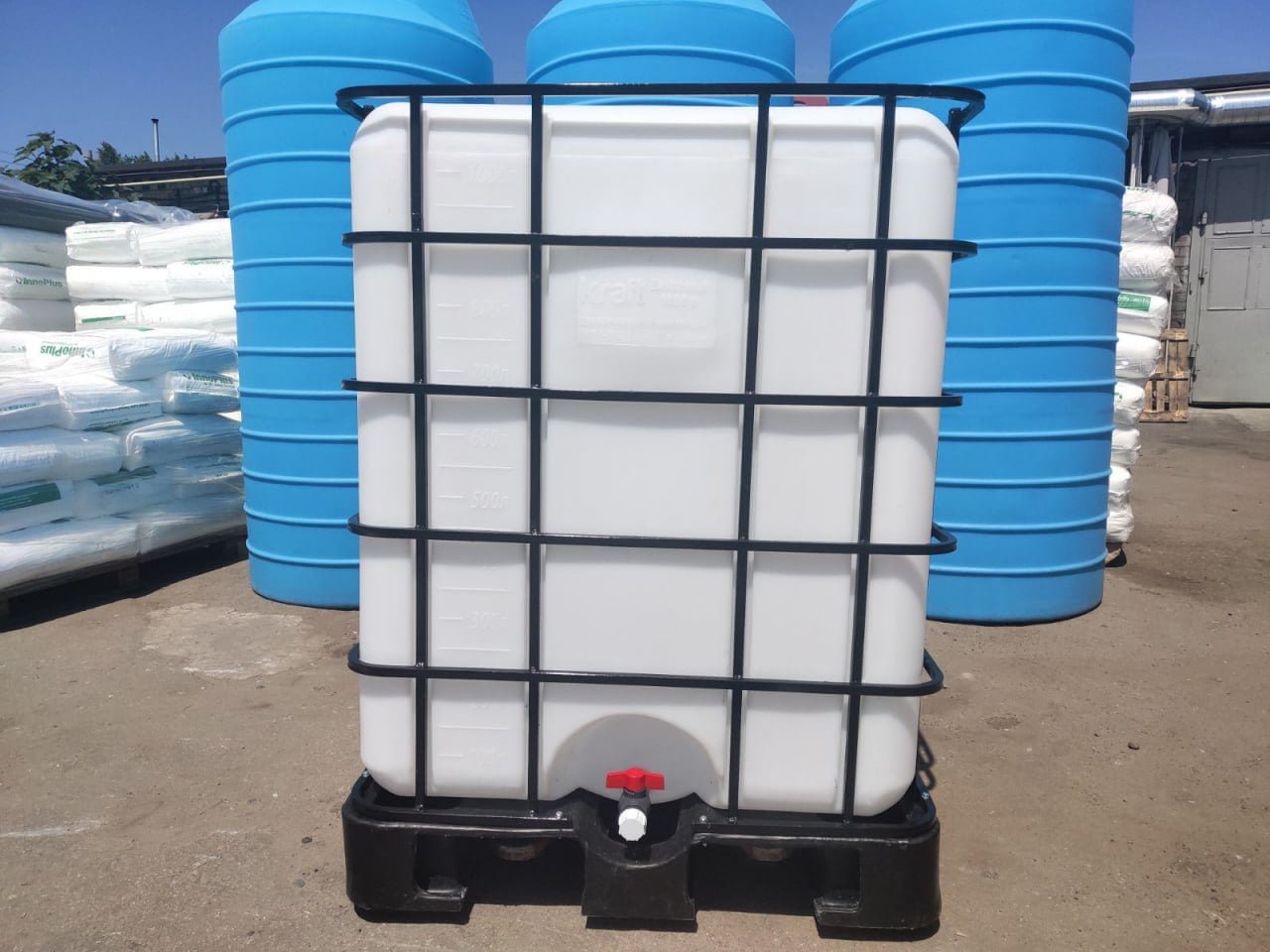
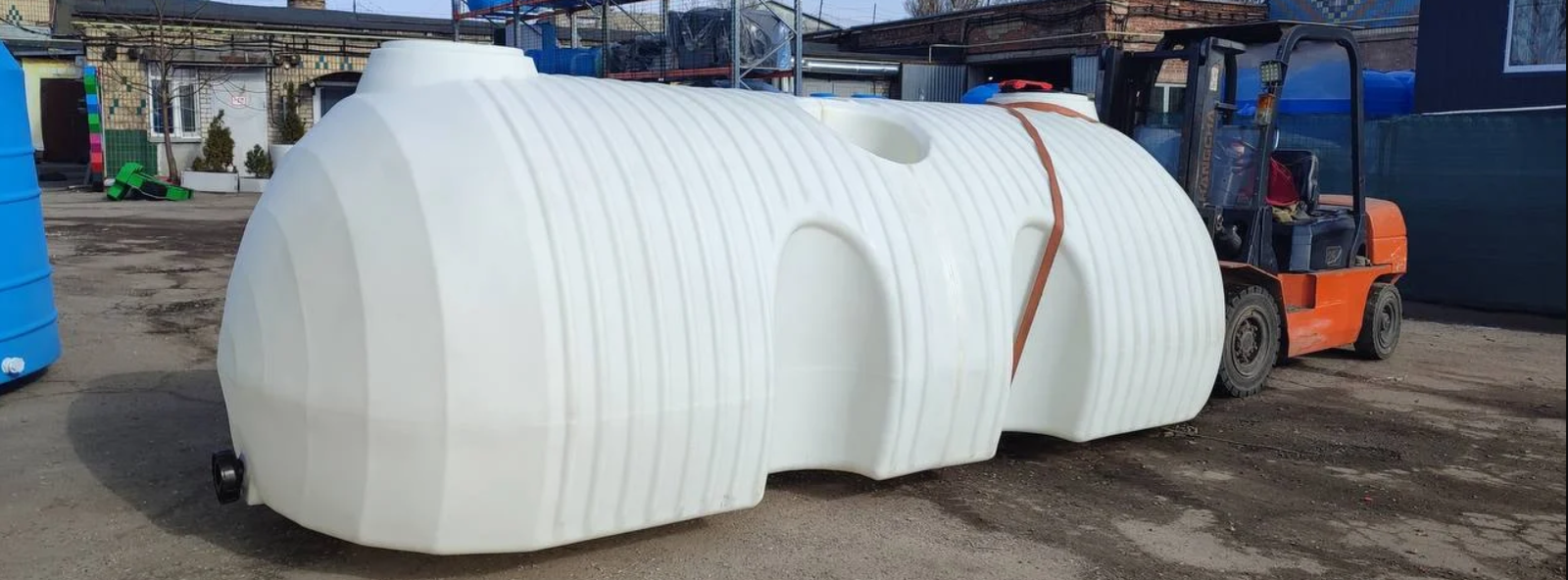
Kraft produces plastic containers using rotational moulding. We produce tanks for storing and transporting water, UAN fertilisers, fuels and lubricants, and agricultural products. We have plastic tanks with a volume of 1-30000 litres with a cross-section in the form of a circle, square, rectangle, with a conical bottom and two hatches, with various fittings and valves. We can produce customised plastic containers according to a customer’s sketch.
The main technology for the production of plastic containers is rotational moulding. Products are manufactured in accordance with ISO 9001:2008. Quality control at each production stage allows us to produce products with improved characteristics. The service life of plastic tanks exceeds 60 years. The yield strength of the material is 17-22 MPa. Resistance to elastic deformation reaches 1200 MPa.
How plastic tanks are made
Rotational moulding is an advanced method of processing polymeric materials that is widely used in Ukraine and abroad. Plastic containers are in demand in the food and chemical industries, agriculture, construction and other sectors. Plastic tanks are used to equip sewage, water supply, irrigation and watering systems. Food-grade plastic is a non-toxic material that is safe for human health and the environment. Rotationally moulded polyethylene has the following advantages
- resistance to ultraviolet radiation;
- increased strength;
- resistance to mechanical loads – shock and weight;
- low weight
- durability;
- chemical inertness – the walls of the tank do not react with the contents.
The production technology is relatively simple and does not require significant material and labour resources, which has a positive impact on production costs and allows us to manufacture inexpensive, competitive products. The production of polyethylene containers using the rotational moulding process takes place in 4 stages:
- Loading polymer raw materials into the mould. Most often, polymers are used in the form of granules or powder.
- Moulding. The mould with the polymer powder is tightly closed and sent to the heating chamber. In the chamber, the mould rotates at a speed of up to 20 revolutions per minute. At the same time, the contents are heated. As a result, the polymer melts and adheres to the walls of the mould. The moulding process is completed when all the polymer material has settled on the walls.
- Cooling. Water or air with a temperature of about 4°C is used to cool the mould. During the cooling process, the mould is constantly rotated to ensure that the material cures evenly along the walls.
- Extraction of the finished tank is the final stage of production. To remove the tank, the mould is opened.
A rotational mould consists of 2, 3 or more parts. The structure is a hollow shell. The mould body is attached to a mechanism that ensures rotation and movement into the heating and cooling chambers. The moulding process takes place at atmospheric pressure. Due to the low pressure force of the material on the walls, there is no need to increase the thickness of the mould body.
Relatively inexpensive equipment for the production of plastic containers means lower costs and production costs. The equipment body is usually made of aluminium, steel and other metals with improved thermal conductivity. The mould is produced by aluminium casting or vacuum metallisation. An alternative technology is electroplating.
The polymer in the mould is heated using the energy of electric heating elements. An alternative heating method is gas combustion. Heating with electric energy is a safe but expensive method compared to using natural gas. The material is heated to a temperature of 300°C. The mould determines the volume and geometric parameters of the finished product. Adjusting the wall thickness of a plastic container is achieved by changing the amount of polymer raw materials added to the mould. The maximum wall thickness of the finished product exceeds 20 mm.
Production of polyethylene containers by rotational moulding: advantages
One of the advantages is the ability to produce tanks of any simple, shaped or complex shape. The technology is suitable for the production of tanks of any size – up to 30 thousand litres. An important advantage is the absence of seams in the tanks. The monolithic structure withstands significant internal and external pressure, and is less prone to cracking and leakage than welded products. Other advantages:
- Waste-free production process. Adherence to the technology helps to minimise the loss of polymeric raw materials. Defective products can be recycled and further used for the production of plastic containers.
- Versatility. Rotational moulding technology is used to produce large and small containers suitable for a variety of commercial applications.
- High productivity. Production of a batch of several pieces is cost-effective.
- The ability to produce tanks with variable wall thickness by adjusting the mould rotation speed.
Plastic products made by rotational moulding are free of internal stress and polymer orientation, which provides increased mould strength and stability.
It will also be interesting
Do you need a consultation?
Fill out the form and we will be in touch to answer your questions







